Introduction
The effects of sugars on our health are the subject of ongoing discussion and medical research. Experts, however, unanimously agree that sugar intake must be kept to a minimum to avoid the onset of serious chronic diseases. In a healthy and balanced diet, sugars must not be lacking, as they are essential for the correct functioning of the body, however, even if not to be eliminated completely, they must be limited to 10% of total daily calories . The quantity corresponds on average to two teaspoons of coffee per day.
Added sugars: limit your intake
The intake of added sugars and free sugars, according to scientific evidence, should be limited to a minimum to stay healthy. In reality, the indication of 10% of daily calories is not a quantity applicable to all types of diet . Therefore, in medicine, there is no threshold that is universally shared and suitable for all people. In addition to the teaspoons of sugar added to coffee or tea, or in the cake dough, the sugars in fruit, milk , some vegetables and the hidden sugars in some foods must also be considered, which dramatically increase the daily quantity consumed.
A diet, in fact, includes different categories and sources of sugars, which can be natural or added. In particular, refined “added sugars” but also “free sugars” naturally present in honey , syrups, fruit and vegetable juices are of greater concern .
“Added Sugars” on the label…
It often happens to read the words “no added sugar” on food labels . To understand what this means, it is useful to understand what is meant by added sugars, i.e. refined sugars that are added to packaged foods during the manufacturing process, in order to obtain a more pleasant flavour, a different texture or greater preservation. In doing so, it is easy to understand how much the amount of sugars and calories contained increase in a modest way, ending up by increasing the consumption of daily sugars in an unconscious way. With added sugars, it increases the glycemic intakeof foods, which causes the onset of various metabolic and cardiovascular diseases.
Added sugars: what are they?
Among the sugars added to foods we find sucrose, table sugar extracted from beets or sugar cane (white or raw); fructose, the fruit sugar; glucose ; maltodextrins ; corn and rice syrups , considered hidden added sugars, as the name may mislead and not suggest sugar.
Natural sugars and added sugars: what are the differences?
Let’s start by saying that from a nutritional point of view, there is no difference between added sugars and natural ones. Both are found in certain foods, such as fruit, milk or honey. What makes the difference, and it is relevant, is the way in which these sugars are taken up (more or less hidden in food) and metabolised by the body. If we consume fruit, we introduce sugars into the body, ie fructose, but also vitamins, mineral salts , antioxidants , flavonoids . Similarly, when we drink a glass of milk, we consume lactose (milk sugar), but also calcium , proteinetc. Added sugars in industrial products, on the other hand, are sugars that are extracted from natural foods, but which lose all other health-promoting nutrients and which are able to counterbalance the absorption of sugar into the blood .
At the metabolic level, natural sugars are processed more slowly by the body, while added sugars enter the bloodstream immediately and cause insulin spikes.
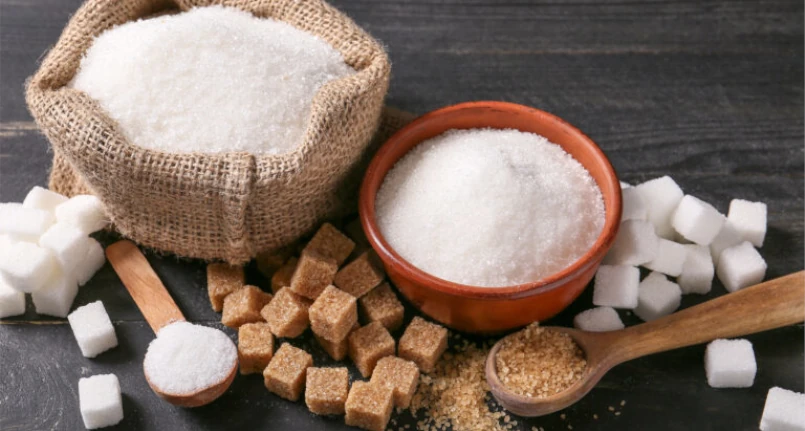
Types of sugar
There are various types of sugar consumed daily. They differ in color, texture and taste . There are white or dark sugars, of the granulated type and with a consistency in more or less fine grains. Sucrose and fructose are the most popular sweet and soluble granular carbohydrates such as table sugar, derived from sugar beets and sugar cane. On the market you can also find other natural sugars such as apple sugar , coconut sugar , etc.
The color of the granulated sugar does not determine its quality, but in general the white one is more refined, since during the production cycle it is deprived of the molasses – typically dark in colour, therefore the brown sucrose and in large crystals, i.e. what is commonly understood as sugar made of raw cane , it has the same characteristics as the white one – also made from beets .
Integral type sugars, on the other hand, are not subjected (or only partially) to centrifugation and refining processes. An example is muscovado , which contains a greater quantity of minerals and vitamins , and a lower glycemic and caloric load .
Icing sugar , on the other hand, is obtained from sucrose in ultra-fine grains with the addition of powdered starch .
Excess sugar: pathologies
Sugar is to be considered a food with a high energy density . An excess in consumption can determine the onset or aggravation of certain pathologies, among which are:
- tooth decay ,
- overweight or obese,
- hypertriglyceridemia ,
- hyperglycemia and type 2 diabetes mellitus ,
- alimentary fatty liver disease ,
- hyperinsulinemia ,
- insulin – resistance .