Introduction
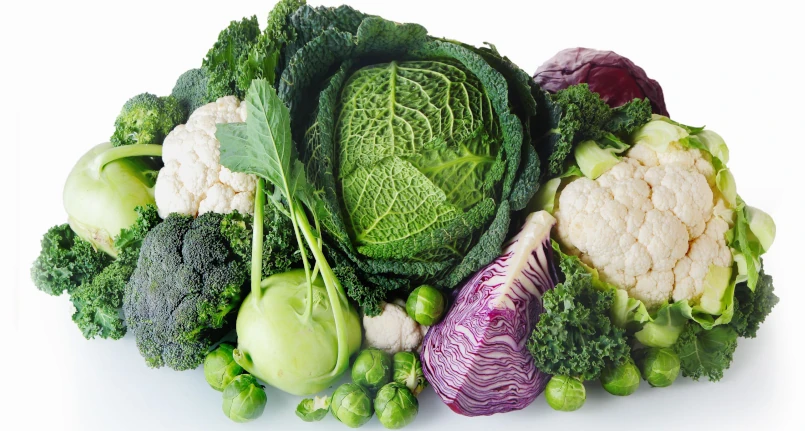
Cruciferous vegetables, or brassicaceae, are vegetables very rich in water and fibre , minerals and vitamins which are essential for the health of the entire organism. Broccoli , cabbage, cabbage, etc. are distinguished by the four-petalled flowers arranged in a cross, from which the name derives. Their antioxidant , anticancer and anti-inflammatory properties derive from the contribution of minerals present in quantities such as: potassium , calcium and phosphorus , but also the content of folic acid , vitamin A , C and K.
Cruciferous: benefits
- Anticancers
- antidepressants,
- antioxidants,
- analgesics ,
- anti-inflammatory,
- cardioprotective
- strengthen the immune system
- improve intestinal function and motility
- modulate the glycemic response to meals
What are cruciferous vegetables?
- Broccoli,
- cauliflower,
- Roman cabbage ,
- cabbage
- red cabbage
- black cabbage
- cabbage
- Brussels broccoli,
- turnips,
- turnip greens ,
- pak choy
- watercress
- radishes
- rocket .
Different vegetables belong to the cruciferous family, whose correct botanical name is brassicaceae (some even less known of the family, or rather not associated with it): broccoli, cabbage, cabbage, turnip tops but also horseradish , mustard , rocket, radishes , watercress . They can be found in the garden and on the fruit and vegetable counter from November to spring.
Nutritional profile
Cruciferous vegetables are very rich in vitamins. Among them there are considerable quantities of: Vitamin C , with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory functions which are at the origin of different types of pathologies. It supports the immune system. Broccoli are those of the cruciferous family that contain the most (twice the orange ). Cons: Vitamin C is largely lost with the heat of cooking . Vitamin K , with an anticoagulant function; and folic acid ( Vitamin B9 ), associated with the production of mood-regulating neurotransmitters . A power is also attributed to cruciferous vegetablesantidepressant .
Broccoli, cabbage, cabbage, etc. contain beta-carotene, the precursor of vitamin A, strengthens the immune system and promotes skin and eye health . The quantity of magnesium , phosphorus, potassium, and above all calcium is also relevant : cabbage, broccoli, etc. are the main vegetable source of this micronutrient.Cruciferous vegetables also contain indole 3 carbinol which favors the production of estrogenic metabolites with an antitumor action;
Sulforaphane, able to prevent the onset of tumors, especially of the digestive system , and to perform a natural pain-relieving action. Also present are lavonoids , including quercetin , a powerful antioxidant capable of increasing cardiovascular protection, and anthocyanins , especially present in purple cabbage; Tryptophan , an essential amino acid in the synthesis of serotonin , i.e. the ” hormone of happiness”.What does the anti-tumor action depend on?
The presence of sulforaphane, a substance which gives the peculiar slightly spicy taste to cruciferous vegetables, has an indirect antioxidant effect if they are eaten raw. The action is in fact that of not directly neutralizing the free radicals , but of promoting the antioxidant activity and some enzymes against the proliferation of tumor cells .
The indoles, also composed of nitrogen , responsible for the pungent smell given off during the cooking of cruciferous vegetables, are able to stimulate the detoxifying action of some enzymes, inhibiting the development of stomach and breast cancer , and generally blocking the development of tumours, intercepting carcinogenic molecules before they damage cellular DNA . Furthermore, indole-3-carbinol is distinguished by its function of inhibiting the activity of estradiol , the precursor of estrogen which, in excess, can cause the onset of hormone-dependent tumors such as those of the breast, uterus and atendometrium .
Benefits of cruciferous vegetables
The protective effect of cruciferous vegetables is above all in contrasting two of the most common and lethal pathologies in Western countries, namely cancer and cardiovascular diseases . Cruciferous vegetables have beneficial properties for intestinal health: they support the functionality of the intestine , thanks to the fiber content which stimulates peristalsis and promotes intestinal motility (in case of abdominal gas , Crohn’s disease , colitis, etc., moderate the consumption of cruciferous vegetables in general). Being the most important sources of calciumin the vegetable world, broccoli, cabbage, etc. are excellent allies for the health of the skeletal system , bones , cartilage and teeth . They are low-calorie, have a high satiating power , support the immune system, and, thanks to the beta-carotene and vitamin A content, promote healthy eyesight and skin.
Cruciferous vegetables in the kitchen
Cruciferous vegetables can be eaten cooked and raw (not all) . By consuming them raw, all the beneficial nutritional characteristics and vitamins are preserved. Radishes , rocket, watercress, cabbage but also with broccoli stems, can be eaten in salads or pinzimonio . Broccoli, cauliflower , cabbage, brussels sprouts , turnip greens, etc. can be cooked in several ways: blanched for up to 8 minutes, steamed , or baked. Black cabbage, savoy cabbage, etc. can be used as an ingredient for soups; cauliflower and broccoli, as well as a tasty side dish, they are blended to obtain creams, soups and purées. Also excellent for seasoning pasta, rice or other cereals , but also in omelettes or timbales.