Introduction
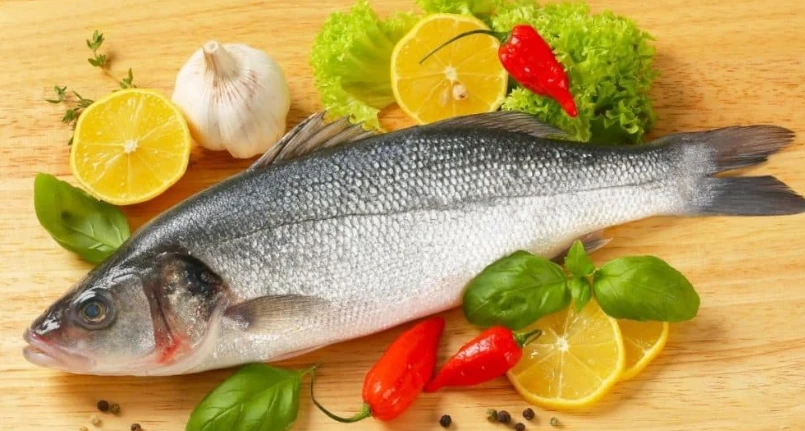
Fish , especially some types, contains high amounts of high-quality protein , making it a good source of this macronutrient while also supplying essential minerals and heart- healthy omega-3 fatty acids . Fish proteins are defined as high biological value peptides (VB=78), as they contain a mapping of essential amino acids (AAE) very similar to that of human proteins. However, it is important to limit the intake of larger fish such as swordfish , as they can contain high levels ofmercury . According to nutrition experts, the recommended daily allowance (RDA) for protein for adult women is 46 grams, while for adult men it is 56 grams. In addition to fish, other foods that are excellent sources of dietary protein include cheese, lean red meats , seeds, poultry, yeast extract , and legumes .
Tuna: the most protein
Of all the fish with a high protein content , tuna is undoubtedly the one that boasts the greatest wealth of this macronutrient. Bluefin and yellowfin tuna species are particularly high in protein, with bluefin tuna offering 29.91 grams of protein per 100 grams of cooked fish, and yellowfin tuna providing 29.15 grams. Canned diet tuna , usually made from a blend of yellowfin tuna and skipjack tuna , is also an excellent source of protein, providing 29.13 grams of protein per 100 grams.
Did you know that among the fish…
Among fish, skate is the least protein food, cod the leanest , tuna the most protein, salmon and eel the fattest, herring the one with the highest creatine content. Crustaceans and molluscs , while containing moderate amounts of cholesterol , are practically devoid of saturated fats and rich in unsaturated fats . Mussels and oysters are also rich in iron and vitamin C.
More protein fish: what are they?
In addition to tuna, other high-protein fish, ranging from about 26 to 29 grams per 100-gram serving, include: anchovies , salmon, halibut , snapper , and tilapia. Swordfish and cod also contain high amounts of dietary protein, each providing about 23 grams per 100 grams of fish. Lobster and other shellfish are also good sources of protein, with lobster providing 26.41 grams per 100 grams. Shrimp and crabmeat are other high-protein marine crustaceans. Although they are usually eaten in smaller quantities than fish meat, eggsfish are also very high in protein, offering approximately 29 grams of protein per 100 grams.
Among the amino acids of fish there is an abundant presence of lysine , the limiting amino acid of cereals and some vegetables. For this reason, the best pairing in the dish is between cereals and fish, vegetables and fish. On the other hand, nutritionists advise against mixing fish and other protein sources such as legumes, meat, cheese or eggs.
Watch out for mercury levels
It is important to choose carefully when selecting high protein fish to limit the risk of mercury exposure. While providing the highest protein content in fish, bluefin tuna, consumed primarily in sushi dishes , has been associated with high levels of mercury. Canned light tuna , on the other hand, while providing only slightly less protein than bluefin tuna, has relatively low levels of mercury. Shrimp, salmon, cod and crab are also low in mercury, while swordfish and red snapper, or large fish in general, contain higher amounts of mercury.
Benefits of fish proteins
Fish proteins have been, and still are, the subject of numerous studies in the nutritional and medical fields. The most corroborated thesis sees the consumption of fish, in particular its fats and proteins, as beneficial and capable of favoring a reduction in the incidence of overweight and an improvement in metabolic parameters ( blood pressure , cholesterolemia , triglycerides , systemic inflammation , overall cardiovascular risk ).
While lipidemia seems to greatly benefit from the nutritional intake of essential polyunsaturated fatty acids of the omega -3 series, present in fish, fish proteins intervene by reducing systemic inflammation (in particular, the C-reactive protein ) and improving sensitivity to insulin ; both of these characteristics make fish proteins an important protection factor against type 2 diabetes mellitus .
Furthermore, fish proteins would have beneficial effects on the bio-regulatory type of metabolism , contributing to a greater sense of satiety thus reducing the consumption of food . This would be due to the ability of fish proteins to stimulate the secretion of gastrointestinal mediators responsible for satiety: cholecystokinin ( CCK) and glucagon peptide-1 (GPL-1). The result is therefore constituted by a physiological improvement in the regulation of body weight .