Folic acid deficiency – a micronutrient also known as vitamin B9 or folacin – is still a rather widespread condition, especially in some areas of the globe.
The impossibility for the body to synthesize this vitamin justifies the extreme importance of an adequate dietary intake.
The body’s reserves of folic acid amount to about 12-15 mg, stored mainly in the liver and only sufficient to compensate for a few weeks of lack of food intake.
Health Risks
Folic acid, as well as vitamin B12 , is essential for adequate cell proliferation and maturation; therefore, the lack of this nutrient first of all affects the tissues with a high degree of proliferation, such as the bone marrow and those of the embryo-foetus. This explains the origin of the two best known and most widespread consequences of folic acid deficiency, represented by macrocytic-megaloblastic anemia and spina bifida in the unborn child .
Folic acid deficiency anemia
In macrocytic-megaloblastic anemia red blood cells become excessively large, assuming an abnormal shape and very short life. Consequently, the person deficient in folic acid complains of weakness and easy fatigue, both physical and mental ( insomnia , irritability and concentration difficulties).
The neurological suffering is also due to the essentiality of folate in the synthesis of some neurotransmitters , such as glutamic acid (an excitatory amino acid released in the central nervous system ).
Spina Bifida
If a pregnant woman does not take adequate amounts of folic acid, irreversible damage to the fetus can result, with an increased risk of neural tube defects (embryonic structure from which the central nervous system originates), the most common of which is spina bifida. The fetus, in turn, removes a large part of the folic acid from the mother, which justifies the integration from when the pregnancy is still being sought until its conclusion. In fact, it is the first stages of development of the embryo-foetus that have the most intense rate of proliferation. In a child with spina bifida, the spinal cord is not tightly enclosed between the vertebrae and can be damaged enough to cause paralysis of the legs.
Homocysteine and cardiovascular risk
A lack of folic acid elevates the cardiovascular risk of the subject, increasing the levels of circulating homocysteine , which in turn increases the possibility of suffering cardiovascular diseases . This condition is common in people who contrast an excessive intake of protein foods ( dairy products , meat , legumes , eggs ) with a low consumption of fresh vegetables .
Other Possible Disorders
Serious folic acid deficiencies have also been linked to depression , skin and mucous membrane lesions, growth and ossification disorders, increased susceptibility to infections, infertility (both male and female), mental retardation and atrophy of the lymphatic organs.
Folic Acid in the Diet
Recommended daily intake
The recommended daily intake of folate is 200-300 µg in adults, 400 µg in pregnancy and 350 µg in breastfeeding .
It is estimated that a balanced diet supplies between 100 and 300 µg of folic acid per day.
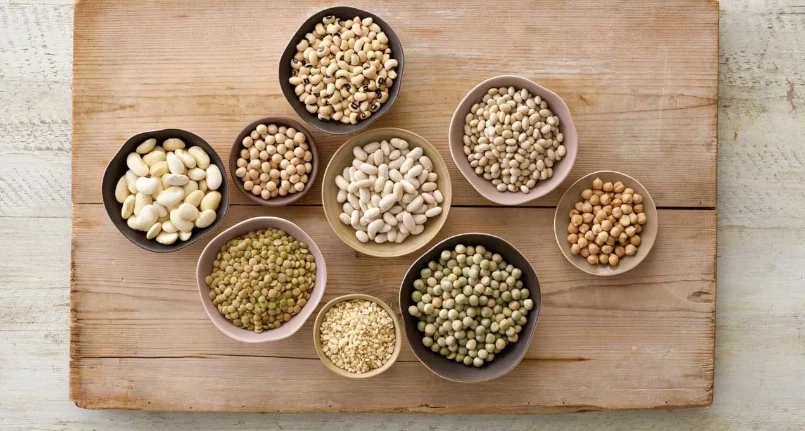
Foods rich in folic acid
Vegetables are particularly rich in this vitamin – especially those with green leaves (cabbage, spinach , cress , etc.) – fruit, whole grains , legumes , liver and brewer’s yeast .
Normally about 40-60% of folic acid of food origin is absorbed, while that taken as a supplement or pharmaceutical product is absorbed for about 80%.
Vitamin B9 is also synthesized by the intestinal bacterial flora .
Losses with Cooking
Cooking losses range from 50 to 95 percent (unfortunately, the most generous food sources, such as cauliflower , Brussels sprouts, and spinach, are the ones that cook the longest).
High temperatures, prolonged soaking and annealing/heating of already cooked vegetables almost eliminate the folic acid content of the fresh food.
Subjects at risk of shortage
At our latitudes, in industrialized countries, folic acid deficiencies of food origin are quite rare and mostly affect the elderly who follow monothematic and repetitive diets, particularly poor in fresh fruit and vegetables , for example due to lack of appetite, social problems, chewing difficulties etc..
Excessive cooking of foods, intensive use of chafing dishes (a typical problem of canteen meals ) and the intake of folic acid antagonist drugs (particularly some antibiotics and chemotherapy), are further predisposing factors for folate deficiency. Even prolonged exposure to light depletes the folic acid content of foods .
Folic acid deficiencies are more frequent among alcoholics and drug addicts ; smoking also has a negative effect . They are also typical of malabsorption syndromes , where the intestine’s ability to absorb nutrients is limited by various diseases and conditions, such as celiac disease ( celiac disease ), intestinal infections, pancreatic disease , Crohn ‘s disease and surgical resections of the intestine .
Deficiency is also frequent in poor tropical and sub-tropical countries (where it is often associated with other nutritional deficiencies) and in those of the far north, where the supply of fresh vegetables is limited for most of the year.
Supplements: When are they needed?
Folic acid supplements are indicated only in deficiency states, as there are no deficiency problems in healthy adults who follow a balanced diet .
Pregnant and breastfeeding women deserve a separate discussion , in which supplementation with folic acid is prescribed by the doctor and must take place under his control and according to the indications given.
To learn more, read: folic acid in pregnancy .
Folic acid supplements are justified in low-calorie diets, in elderly alcoholics or malnourished, in alcoholics and in patients with malabsorption. They can also be prescribed in high-level athletes in order to solve anemia problems.
In some supplements or pharmaceutical products, folic acid is combined with iron , as the association between the two types of deficiency is not rare, possibly ascorbic acid and vitamin B12 (with the aim of supplying the body with the micronutrients necessary for optimal synthesis of red blood cells).
The normally recommended intake doses for folic acid supplements are 400mcg per day.
Folic acid: the best supplements according to online reviews
There are many natural products on the market designed to integrate the right amount of folic acid, in terms of food, prevention and pregnancy. Here are the ones most appreciated by those who bought them online:
Inofert is a food supplement based on folic acid and inositol, useful for regulating the functionality of the ovaries and especially indicated for women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome . It can also be taken as an adjuvant in conditions of insulin resistance , pre-diabetic states and in type II diabetes. This supplement does not contain sucrose, lactose, or gluten. The package contains 20 sachets: the recommended dose is one sachet per day to be dissolved in a glass of water at room temperature, drunk in small sips, regardless of meals.
Nutravita ‘s Folic Acid supplement provides 400mcg of this important element per serving (1 tablet). Each pack contains 400 vegan tablets for 13 month coverage. The tablets contain no synthetic fillers or binders. Nutravita’s products are particularly popular with Amazon users because the company relies on a dedicated team of pharmacologists, chemists and scientific researchers, who are committed to sourcing the best ingredients, free from artificial colors and flavors, GMOs and allergens such as gluten , soy , lactose and peanuts.