Introduction
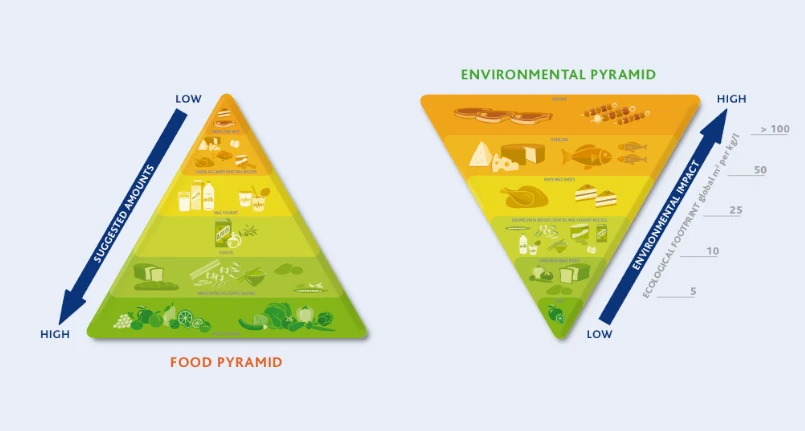
A graphic model explains exhaustively and clearly the relationship between food and the environment. A correlation highlighted in the so-called Double Food Pyramid , created by the Barilla Center for Food & Nutrition and Food Tank with the patronage of the Italian National Commission for UNESCO.
The two food pyramids, side by side, that of the Mediterranean diet with the vertex facing upwards and the environmental one upside down, allow us to understand how much a balanced diet can promote good health, longevity and well-being, while reducing the environmental impact . This results in a reduction of carbon emissions , respecting local traditions and food systems.
The double food pyramid therefore underlines the importance of a healthy lifestyle. The daily food choices that everyone makes must not only be oriented towards physical well-being, but also towards that of the planet.
The Food Pyramid
The food pyramid, the better known of the two, is based on the principles of the Mediterranean diet , i.e. the sustainable food model par excellence, with nutritional value recognized by science.
At the base of this pyramid is the largest area, which houses the foods that should be eaten more frequently and have the most benefits for health: vegetables, fruit, dried fruit, unrefined cereals , legumes and extra virgin olive oil .
In the middle of the pyramid, on the other hand, are the foods that should be eaten moderately, on a weekly basis: fish , dairy products , eggs and white meat .
Finally, at the top of the pyramid are foods whose intake should be reduced or limited to once a week: red meat and more generally foods rich in saturated fats .
The Environmental Pyramid
In the model of the Double Food Pyramid there is, in fact, a second pyramid alongside that of the Mediterranean regime. It is an inverted food pyramid, called the environmental pyramid which classifies foods according to the environmental impact obtained from their production and cultivation .
In this case, at the top we find the largest area with all those foods that are most harmful to the environment. The study shows that there is an inverted correlation between the best foods for health and their impact on the environment: foods with a lower environmental impact are also the ones most recommended from a nutritional point of view and which must be consumed in abundance following a healthy and balanced diet.
The environmental impact of food: three indicators
To elaborate which foods and to what extent their production can impact on the planet, the researchers used Life Cycle Assessment ( LCA ), a proven technique, based on objective parameters, able to evaluate the energy consumption and the environmental load of a process, considering the entire production chain.
There are three different environmental indicators considered to obtain data on the environmental impact of each individual food.
- Carbon footprint: quantifies carbon dioxide and greenhouse gas emissions responsible for climate change;
- Water footprint: the total volume of fresh water used to produce a given type of food;
- Ecological footprint: an indicator capable of measuring man’s impact on the environment in the production process. To determine this figure, many factors are taken into consideration, such as, for example: sum of cultivated lands, pastures, forests and fishing areas necessary to produce the food and energy essential for human activities; production and disposal of waste emitted; construction of infrastructures aimed at production.
Limit what harms the environment on your plate
The result obtained from the research is clear: starting from a survey of the international scientific literature, the two pyramids can be clearly read side by side. At the top are the foods with the greatest environmental impact and, at the bottom, those least harmful to the planet. By relating the two scales of the Food-Environmental Double Pyramid, it is easy to understand how much the foods for which a higher consumption is recommended (fruit, vegetables, legumes, unrefined cereals), in general, are also those that have an impact on the lower environment. Conversely, the foods for which limited consumption is recommended ( red meat , saturated fats ) are the same ones that have the greatest environmental impact.
Food and environment: what correlations?
The study developed on the model of the double food and environmental pyramid therefore evaluates the environmental impact of foods that are part of the daily diet. This model can be replicated all over the world and is able to evaluate local crops and production systems. Foods have been associated with the values of the corresponding Ecological Footprint, i.e. the ecologically productive surface necessary to obtain all the resources used for production (Ecological Footprint). A similar result was obtained by estimating the Carbon Footprint of foods, ie the quantity of greenhouse gases emitted into the atmosphere (Carbon Footprint).