Foods that contain phytosterols all belong to the plant world (with the exception of ADDED foods).
Phytosterols
What are
Phytosterols are sterol molecules having a structure very similar to that of cholesterol , a lipid typically of animal origin.
How they act
The beneficial action of foods that contain phytosterols is to bind cholesterol inside the intestinal lumen, preventing its absorption and favoring its faecal expulsion .
In Food
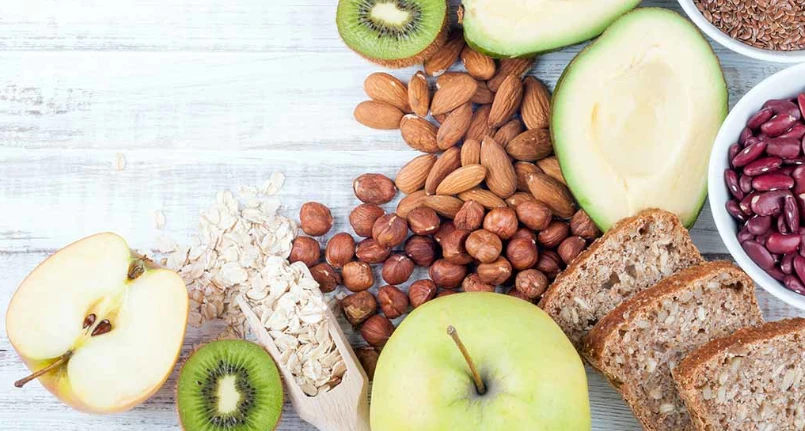
Foods Rich in Phytosterols
Foods that contain phytosterols are vegetable oils , dried fruit ( walnuts , hazelnuts , almonds , etc.), legumes , some seeds, cereals , fresh fruit , vegetables and recently also added yoghurt (see EC regulation 2004).
Average intake in the diet
- The intake of phytosterols with the diet normally varies between 150 and 450 mg per day, in relation to the dietary habits of the subject; for example in the diet of vegetarians the intake of phytosterols can rise up to 700 mg/day and beyond. The most common phytosterols in human nutrition are beta-sitosterol, campesterol and stigmasterol, which contribute 65%, 30% and 3% respectively to the total dietary intake. A yogurt enriched with phytosterols widely advertised in Italy declares a content of 1.6 g of phytosterols per serving (one vial).
Functional foods
Foods that have good quantities of phytosterols are considered pharmaceuticals or functional foods as they fall into the category of foods containing nutraceutical molecules , therefore medicinal; nutraceutical molecules are food substances with proven beneficial and protective characteristics against both physical and psychological health of the individual.
Against high cholesterol
Foods containing phytosterols can be useful in the integrative or adjuvant treatment of lipoprotein disorders; as a result they were included in the therapeutic lifestyle change guidelines; it is possible to state that in the medium and long term, the consumption of functional foods containing phytosterols can reduce hypercholesterolemia by about 10%, but the effectiveness of foods containing phytosterols is closely linked to the method of intake; in particular, these must necessarily be consumed EVERY DAY, BEFORE the two or three main meals of the day.
An important caveat…
Phytosterols cannot replace drug therapy against hypercholesterolemia; moreover, their consumption DOES NOT allow you to adopt incorrect eating habits and, in general, DOES NOT effectively compensate for genetic and/or family pathologies.