Alcoholism
What is alcoholism ?
Alcoholism is the term commonly attributed to those who abuse alcoholic beverages . In reference to its enormous importance in the health field, alcoholism was already included in 1980 among the abuse syndromes described in the “Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders ” – to date in the IV edition (DSM-IV); Initially, this disorder was framed as ” alcohol abuse and dependence ” and only later was the wording corrected to ” alcohol (ethanol) dependence and syndrome “.
Indeed alcoholism is a pathological syndrome in every respect; it represents a set of symptoms and clinical signs generated by the systemic impairment of the organs which, following a chronic ethyl alcohol intoxication , lose functionality and anatomical integrity.
In subjects with alcoholism, acute or chronic ethanol intake is distinguished from the ordinary by large quantities, and compulsive behavior .
Harms of alcoholism
Short-term and long-term effects and symptoms of alcoholism include:
- Damage to the Central Nervous System ( CNS ) manifested in unbridgeable gaps in memory and inability to learn, also identifiable in the form of pins and needles in the hands and feet ; in advanced stages, loss of manual use.
- Esophagitis and/or esophageal ulcers
- Lesions of the gastric and duodenal mucosa : gastritis and/or ulcers
- Muscle weakness or atrophy and related myocardial infarction
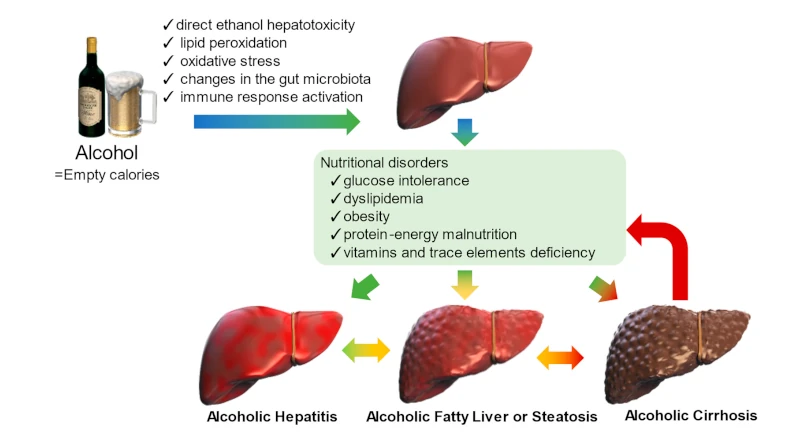
- Liver damage with symptoms of: pain in the right hypochondrium ( alcoholic steatosis ), abnormal redness of the hands and feet and inappetence. Abnormal liver function causes : changes in blood lipid profile, changes in plasma proteins and related ascites
- Pancreatic damage : tendency to develop diabetes and increased risk of pancreatitis
- In men, testicular atrophy and related impotence and gynecomastia (due to hormonal changes )
- Increased episodes of vomiting and diarrhea (malabsorption and malnutrition)
- Alteration of intestinal function: impairment of the brush border (malabsorption and malnutrition) and pro-inflammatory irritative effect of the mucosa
- Increased cancer risk in different districts: mouth, throat, esophagus , stomach and liver, but it can also contribute to those of the breast and colon .
Vitamin deficiencies
What are vitamin deficiencies ?
Vitamin deficiency or vitamin deficiency is a state of malnutrition that implies an insufficient intake of vitamins. Whether it affects water-soluble or fat-soluble molecules, the low intake of vitamins has negative repercussions on health. In truth, not all vitamin deficiencies are created equal; they can be distinguished according to the number of vitamins involved – single or multivitamin deficiencies – and the extent of the deficiency – hypovitaminosis or avitaminosis. It should be emphasized that, to date, in developed countries, serious vitamin deficiencies are extremely rare and correlated to situations that are completely different from normality; hypovitaminosis typical of alcoholism, EDs, of those suffering from serious pathologies of the digestive system are frequentand poorly self-sufficient elderly people . Conversely, in third and fourth world countries, such malnutrition-undernutrition is much more widespread and linked to the insufficiency of economic or environmental resources – water, vegetation, animals, etc.
Alcoholism and vitamin deficiencies
Alcoholism: what vitamin deficiencies?
The alteration of the absorption potential and the tendency to episodes of diarrhea and vomiting can easily lead to stages of even severe malnutrition. The components that seem to be most affected by alcohol at a nutritional level are vitamins, in particular, the most frequent deficiencies concern: thiamine (vit B1), riboflavin (vit B2), niacin (vit PP) and folic acid (vit bc).
In alcoholism, vitamin deficiencies cause rather serious effects and symptoms; thiamine (as well as riboflavin, niacin and folic acid) is a water-soluble vitamin which is absorbed in the intestine ; considering that in the alcoholic the absorption and metabolization capacity are seriously compromised, in cases of serious abuse it is frequent that symptoms of malnutrition in an advanced stage appear.
Alcoholism and thiamine or vitamin B1 deficiency
The primary effects of thiamine -induced avitaminosis (due to alcoholic etiopathogenesis ) are reflected on the CNS with the worsening of nerve conduction efficiency, and on other tissues by reducing the enzymatic metabolization capacity of alcohol itself .
Alcoholism and riboflavin or vitamin B2 deficiency
Riboflavin is also absorbed in a similar way and therefore its absorption is compromised by alcohol abuse; the worsening of the uptake of vit B2 mainly causes a non-selective alteration of the mucous membranes which manifests itself clearly in skin lesions around the nose and mouth.
Alcoholism and niacin or vitamin PP deficiency
Intestinal malabsorption also seems to significantly involve niacin , the prolonged deficiency of which negatively affects the maintenance of skin integrity, further worsening intestinal and nervous function.
Alcoholism and folic acid deficiency
With regard to folic acid , a fundamental vitamin for the synthesis of nucleic acids , anemic forms of a megaloblastic nature, alteration of the mucous membranes and worsening of diarrhea frequently occur ; in similar conditions, the pregnant woman (who for the gestation needs an intake of folic acid higher than the norm) has very high percentages of suffering abortion or fetal malformations.
Conclusions
Alcoholism and vitamin deficiencies: conclusions
It is clear that alcoholism has a negative impact on the nutritional situation, determining directly (malabsorption) and indirectly (inappetence and anorexia induced by alcoholic psychosis ) the lack of essential elements for maintaining good health. The first symptoms that indicate the state of vitamin deficiency are dermatological, intestinal and nervous; to these are added essential deficits of ac. fats, amino acids and mineral salts . In the treatment of the alcoholic, physiological nutritional restoration is essential for systemic improvement as intestinal alteration is both cause and effect of the vitamin deficiency .